Where are the seas of the Atlantic Ocean. What continents are washed by the Atlantic Ocean? What countries are washed by the Atlantic Ocean
Official name: Atlantic Ocean
Water volume: 329 700 000 cubic km
Total area: 79 721 274 sq. Km
Coastline: 111 866km
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest after a quiet one. This ocean, which got its name from the mythological island of Atlantis, shares or, rather, connects in its northern part the most populated and most civilized parts of the world; therefore, despite the fact that it is the most turbulent of all the seas, the Atlantic Ocean differs in same time and the greatest revival.
It washes the shores of Africa, North and South America and Europe.
The area covered by the Atlantic Ocean alone is 79,721,274 square kilometers, and together with the coastal and Mediterranean seas (Mediterranean, Baltic, Northern, Irish-Scottish and St. Lawrence Bay) it equals 88,634,133 square kilometers. The length from north to south is 13,335 km, the greatest width, between Senegambia and the Gulf of Mexico, is 9,000 km, the smallest is 1,445 km between Norway and Greenland (7,225 km. Between Georgia and Africa, 7,225 km between Cape Horn and Cape Dobra Hope, 5 550 km between the capes of San Roca and Sierra Leone).
In the northern part of the ocean, the shores are cut by the St. Lawrence Bay, the Gulf of Mexico and the Carib Bays, just like the European mainland Baltic and German seas, the Gulf of Aquitaine, the Mediterranean and the Black Seas, the southern shores of the South American as well as African ones seem to be on the contrary, very few are indented. Leaving the Gulf of Guinea corresponds to the protrusion of Brazil, also to the protrusion of Senegambia and Sudan - the cut of the Antilles Sea. According to the wealth of oceanic islands, towering among the open sea, the ocean is significantly inferior to the Pacific only near North America and islands abound on the coast. Important stations are: Iceland and the Faroe Islands between Europe and Polar America; and the Bermuda group between Europe and the middle and southern part of North America; Ascension Islands, St. Helena, and between Africa and South America; Finally, the Falkland Islands.
Seas: Baltic, North, Mediterranean, Black, Sargasso, Caribbean, Norwegian. Large bays: Biscay, Guinean, Mexican. The largest straits: Davis, Danish, Drake. The largest islands are the British, Iceland, Newfoundland, the Greater and Lesser Antilles, the Canary Islands, Cape Verde, and the Falkland Islands (Maldives).
The greatest depth is the Milwaukee Basin in the Puerto Rico Trench (-8,605 m).
The main surface currents: warm - North Passat, Gulf Stream, North Atlantic and cold - Labrodorskoye and Canary in the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean; warm - South Passat, Brazilian and cold - West Winds and Bengal in the South Atlantic.
Large ports: Rotterdam (Netherlands), New York, Houston (USA), Marseille (France), Hamburg (Germany), Genoa (Italy), London (United Kingdom), Buenos Aires (Argentina), St. Petersburg (Russia), Ilyichevsk (Ukraine ).
Most interesting facts about the atlantic ocean:
1. The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest ocean of our planet after the Pacific Ocean.
2. An interesting fact about the Atlantic Ocean is that its modern name is derived from the name of the titan - Atlanta, the hero of Greek mythology, who held the sky on his shoulders. Earlier, this ocean was called the West. The first navigator to cross the Atlantic was Columbus.
3. Atlantis - the mainland, according to legend, existed in antiquity on the territory of the Atlantic Ocean. According to legend, as a result of changes on the planet, he went under the water, along with all the inhabitants. Officially, Atlantis is considered to be invented by Plato as an image of the depravity of people.
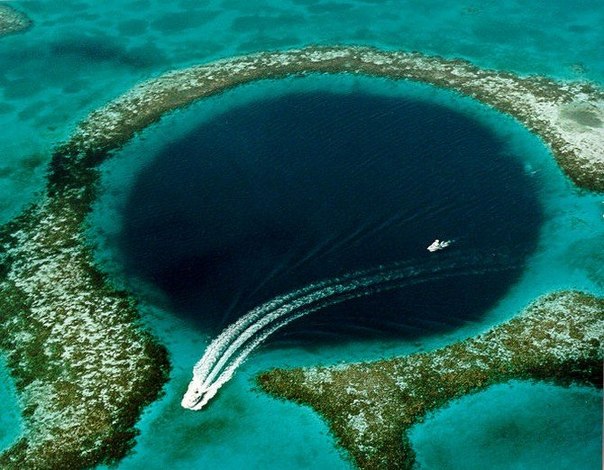
4. One of the most beautiful "attractions" of the Atlantic Ocean is a huge underwater hole, which is located in the center of the atoll of the Belize barrier reef and is an unforgettable sight for all who have seen it. The name she was given because of the sharp border of dark and light water. It seems that the depth in the center of the bowl is many kilometers, but in fact it is about 120 m.

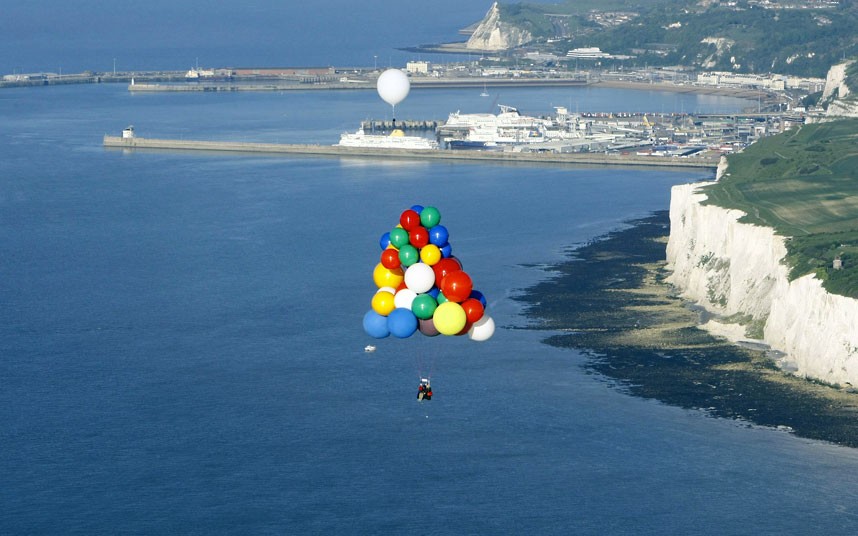
5. The Atlantic Ocean has always attracted travelers and explorers. One of these brave souls is Jonathan Trapp, who in the near future intends to overcome 4020 km alone, hanging on a bunch of 370 balloons filled with helium. The flight across the Atlantic has been a challenge for aeronauts for decades. Five other volunteers died trying to make such an attempt, and no one crossed the Atlantic, clinging to a bunch of balloons.

6. An interesting fact is that, according to the researchers, the amount of ocean water in the Atlantic is approximately equal to the amount of water in the ice of Antarctica.
7. In the north of the Atlantic is the largest island in the world Greenland. The farthest island on Earth is also located in the Atlantic Ocean. This is the island of Bouvet, which with the Cape of Good Hope share 1600 km.
8. In the Atlantic Ocean there is a sea that does not have coastal boundaries - Sargasso. Its boundaries outline only ocean currents.
9. The Bermuda Triangle, with which many mysteries and legends of the disappearance of ships and ships are connected, is located in the Atlantic Ocean.
10. According to some scientists, the Atlantic Ocean is rapidly "aging" and may soon disappear from the face of the Earth. A group of Australian researchers found rapidly forming subduction zones on the ocean floor. Usually they are a sign of "aging". Scientists do not exclude the possibility that the “dying” Mediterranean Sea is to blame for their education. It seems quite surprising - in fact, according to the generally accepted point of view, this reservoir is quite young.
Usually, new oceans are born when the continents are torn apart, and hot magma pours out of the faults, which solidifies and turns into oceanic crust. This is how the Atlantic Ocean was born, when in the Mesozoic era the supercontinent Pangea split into the southern mainland of Gondwana and the northern one - Laurasia. Conversely, the old oceans are dying in the period when the continents collide, and the oceanic crust under their pressure sinks back into the mantle. Thus, the aforementioned Tethys Africa disappeared and India approached Eurasia, completely leaving no place for the water basin that previously divided these continents.
The area of the Atlantic Ocean with seas is 91.7 million km 2, which is about a quarter of the World Ocean. It has a peculiar configuration. It expands in the northern and southern parts, narrows in the equatorial region to 2,830 km and has a length of 16,000 km from north to south. It contains about 322.7 million km 3 of water, which corresponds to 24% of the volume of the oceans. About 1/3 of its area occupies the mid-ocean ridge. The average depth of the ocean is 3597 m, maximum 8742 m.
In the east, the ocean boundary extends from the Statland Peninsula (62 ° 10 ¢ N 5 ° 10 ¢ E) along the coast of Europe and Africa to Cape Igolny and further along the meridian of 20 ° E. to the intersection with Antarctica, in the south - along the coast of Antarctica, in the west - along the Drake Strait from Sternek metro station on the Antarctic Peninsula to Horn m. on a conditional line - the southern entrance cape of the Hudson Strait, Cape Ulsingham (Baffin Island), Cape Bornil (Greenland), Cape Gerpir (Iceland Island), Fugle Island (Faroe Archipelago), Island Flagl (Island of Shetland), Statland Peninsula (62 ° 10 n. Sh. 5 ° 10 e).
In the Atlantic Ocean, the coastline of Europe and North America is characterized by significant irregularity, the outlines of the shores of Africa and South America are relatively simple. There are several Mediterranean seas (the Baltic, Mediterranean, Black, Marmara, Azov) and 3 large gulfs (Mexican, Biscay, Guinea) in the ocean.
The main groups of islands of the Atlantic Ocean are of continental origin: Great Britain, Ireland, Newfoundland, Great and Small Antilles, Canary Islands, Cape Verde, Falkland. A small area is occupied by volcanic islands (Iceland, Azores, Tristan da Cunha, Saint Helena, etc.) and coral (Bahamas, etc.).
Features of the geographical position of the Atlantic Ocean predetermined its significant role in the lives of people. This is one of the most developed oceans. Since ancient times, it has been studied by man. Many theoretical and applied problems of oceanology were solved on the basis of research carried out for the first time in the Atlantic Ocean.
Geological structure and bottom relief. Submarine continental margins occupy about 32% of the area of the Atlantic Ocean. The most significant areas of the shelf are observed off the coast of Europe and North America. Off the coast of South America, the shelf is less developed and expands only in the Patagonia region. The African shelf is very narrow with depths from 110 to 190 m, in the south it is complicated by terraces. In high latitudes on the shelf, glacial forms of relief are widespread, due to the impact of modern and quaternary continental glaciations. In other latitudes, the shelf surface is dropped by accumulative-abrasive processes. Practically in all shelf areas of the Atlantic there are relict flooded river valleys. Of the modern landforms, sand ridges formed by tidal currents are most widely represented. They are typical for the North Sea shelf, the Channel, North and South America. In equatorial-tropical latitudes, especially in the Caribbean Sea, near the Bahamas and the coasts of South America, coral structures are common.
The slopes of the submarine continental margin in the Atlantic Ocean are mainly expressed by steep ledges, often of a stepped profile. They are everywhere dissected by submarine canyons and are sometimes complicated by marginal plateaus. The continental foot in most regions is represented by a sloping accumulative plain lying at depths of 3000–4000 m. In some regions, there are large cones of removal of turbid flows, among which are the cones of submarine canyons of the Hudson, Amazon, Niger and Congo.
Transition zone in the Atlantic Ocean is represented by three areas: the Caribbean, Mediterranean and South Sandwich or the Scotia Sea.
The Caribbean region includes the sea of the same name and the deep-sea part of the Gulf of Mexico. There are numerous uneven-age island arcs of complex configuration and two deep-sea troughs (Cayman and Puerto Rico). The bottom relief is very complex. Island arcs and submarine ridges divide the Caribbean into several basins with depths of about 5,000 m.
The transition region of the Scotia Sea is a section of the underwater margin of the continents fragmented by tectonic movements. The youngest element of the area is the island arc of the South Sandwich Islands. It is complicated by volcanoes and is bordered from the east by the same deep-sea trench.
The Mediterranean region is characterized by the dominance of the continental-type crust. The subcontinental crust is found in the form of separate sections only in the deepest depressions. The Ionian Islands, Crete, Kasos, Karpathos and Rhodes form an island arc, followed from the south by the Hellenic Trench. The Mediterranean transition region is seismic. There are active volcanoes, including Etna, Stromboli, Santorini.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge starts off the coast of Iceland called Reykjanes. In terms of it, it is S-shaped and consists of the northern and southern parts. The length of the ridge from north to south is about 17,000 km, the width reaches several hundred kilometers. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is distinguished by significant seismicity and intense volcanic activity. Most earthquake foci are confined to transverse faults. The axial structure of the Reykjanes Ridge is formed by a basalt ridge with mild rift valleys. At latitude 52-53 ° c. sh. it is crossed by Gibbs and Reykjanes transverse faults. From here begins the North Atlantic Ridge with a well-pronounced rift zone and numerous transverse faults. In the equatorial ridge, it is broken by a particularly large number of faults and has a sublatitudinal strike. The South Atlantic Ridge also has a well-defined rift zone, but is less dissected by transverse faults and more monolithic than the North Atlantic. The volcanic plateaus of Ascension, the islands Tristan da Cunha, Gough, Bouvet are confined to it. At Bouvet Island, the range turns to the east, passes into African-Antarctic, and joins the ridges of the Indian Ocean.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge divides ocean bed into two almost equal parts. They in turn intersect with transverse uplifts: Newfoundland Range, Uplift of Ceara, Rio Grande, Cape Verde Islands, Guinea, Whale Ridge, etc. In the Atlantic Ocean there are 2500 separate seamounts, of which about 600 are located within the ocean floor. A large group of seamounts is confined to the Bermuda Plateau. In the area of the Azores islands, guyot and volcanic mountain ranges are widely represented. Mountain structures and uplifts divide the ocean floor into deep-sea basins: Labrador, North American, Newfoundland, Brazilian, Iberian, West European, Canaryian, Angola, Cape. Flat abyssal plains are characteristic of the bottom relief of the basins. Abyssal hills are typical in the areas of the basins adjacent to the mid-ocean ridges. In the north of the Atlantic Ocean, as well as in tropical and subtropical latitudes, there are many cans 50–60 m deep. On a larger area of the ocean floor, the thickness of the sedimentary layer exceeds 1 km. The most ancient deposits of the Jurassic age.
Bottom sediments and minerals.Among the deep-sea sediments of the Atlantic Ocean, foraminifera dominate, occupying 65% of the ocean floor area. Due to the warming effect of the North Atlantic Current, their range extends far to the north. Deep red clay covers about 26% of the ocean floor and lies in the deepest parts of the basins. Pteropod deposits are more common in the Atlantic Ocean than in other oceans. Radiolaria silts are found only in the Angolan Basin. Silica diatom silts are widely represented in the south of the Atlantic, with a silica content of up to 72%. In some areas of equatorial-tropical latitudes, coral muds are observed. In shallow areas, as well as in the Guinean and Argentine basins, terrigenous sediments are well represented. Pyroclastic sediments are widespread on the shelf of Iceland and the Azores Plateau.
The sediments and bedrock of the Atlantic Ocean have a wide range of minerals. In the coastal waters of South-West Africa there are deposits of gold and diamonds. Huge deposits of monazite sands have been discovered off the coast of Brazil. Large deposits of ilmenite and rutile are observed off the coast of Florida, iron ore from Newfoundland and Normandy, and cassiterite off the coast of England. Iron-manganese nodules are scattered on the ocean floor. In the Gulf of Mexico, Biscay and Guinea gulfs, the North Sea, the Maracaibo lagoon, the Falkland Islands region and a number of other places, oil and gas fields are being developed.
Climate The Atlantic Ocean is largely determined by the characteristics of its geographical location, a peculiar configuration, and conditions of atmospheric circulation.
Annual total amount solar radiation varies from 3000–3200 MJ / m 2 in subarctic and antarctic latitudes to 7500–8000 MJ / m 2 in equatorial-tropical. The value of the annual radiation balance ranges from 1500-2000 to 5000-5500 MJ / m 2. In January, a negative radiation balance is observed to the north of 40 ° C. w .; in July - south of 50 ° S. sh. The maximum monthly value (up to 500 MJ / m 2) reaches the balance in the tropics, in January in the southern hemisphere, in July in the northern hemisphere.
The pressure field over the Atlantic Ocean is represented by several atmospheric centers. In temperate latitudes of the northern hemisphere, the Icelandic minimum is located, more active during the winter period. In the subpolar region of the southern hemisphere, the Antarctic low pressure belt is distinguished. In addition, the Greenland High and the Antarctic High Pressure Region have a significant influence on the climate formation at high latitudes of the Pacific Ocean. In the subtropical latitudes of both hemispheres above the ocean are the centers of two permanent pressure peaks: the North Atlantic (Azores) and South Atlantic. Along the equator is equatorial depression.
The location and interaction of the main pressure centers determines the system of the prevailing winds in the Atlantic Ocean. East winds are observed in high latitudes off the coast of Antarctica. In temperate latitudes, westerly winds prevail, especially in the southern hemisphere, where they are most constant. These winds cause a significant recurrence of storms throughout the year in the southern hemisphere and in winter in the northern hemisphere. The interaction of subtropical maxima and equatorial depression causes the formation of trade winds in tropical latitudes. The repeatability of the trade winds is about 80%, but they rarely reach the storm speed. In the tropical part of the northern hemisphere in the Caribbean, the Lesser Antilles, the Gulf of Mexico and Cape Verde there are tropical cyclones, with hurricane winds and heavy rains. On average, there are 9 hurricanes per year, most of which occur in the period from August to October.
Seasonal changes are well traced in the Atlantic Ocean. air temperature. The warmest months are August in the northern and February in the southern hemispheres, the coldest are February and August respectively. In winter, in each hemisphere, the air temperature in equatorial latitudes drops to +25 ° C, in tropical - to +20 ° C and moderate - to 0 - - 6 ° C. The annual amplitude of air temperature at the equator is not more than 3 ° С, in subtropical up to 5 ° С, in moderate ones up to 10 ° С. Only in the extreme northwest and south of the ocean, where the influence of the adjacent continents is most affected, does the average air temperature of the coldest month fall to -25 ° C, and the annual temperature amplitude reaches 25 ° C. In the Atlantic Ocean, there are noticeable anomalies in the sublatitudinal air temperature distribution along the western and eastern coasts of the continents, due to the influence of ocean currents.
Differences in atmospheric circulation over the Atlantic affect the cloud pattern and precipitation in its waters. The maximum cloudiness over the ocean (up to 7-9 points) is observed in high and temperate latitudes. In the area of the equator, it is 5-b points. And in subtropical and tropical latitudes decreases to 4 points. The amount of precipitation in polar latitudes is 300 mm in the north of the ocean and 100 mm in the south, in temperate - rises to 1000 mm, in subtropical and tropical - varies from 100 mm in the east to 1000 mm in the west and equatorial - reaches 2000-3000 mm.
Characteristic for temperate latitudes of the Atlantic Ocean are thick fogsformed by the interaction of warm air masses with a cold surface of water. Most often they are observed in the area of the island of Newfoundland and off the south-western shores of Africa. In the tropical zone, fogs are rarely observed and are most likely near Cape Verde Islands, where the dust removed from the Sahara serves as condensation nuclei for atmospheric water vapor.
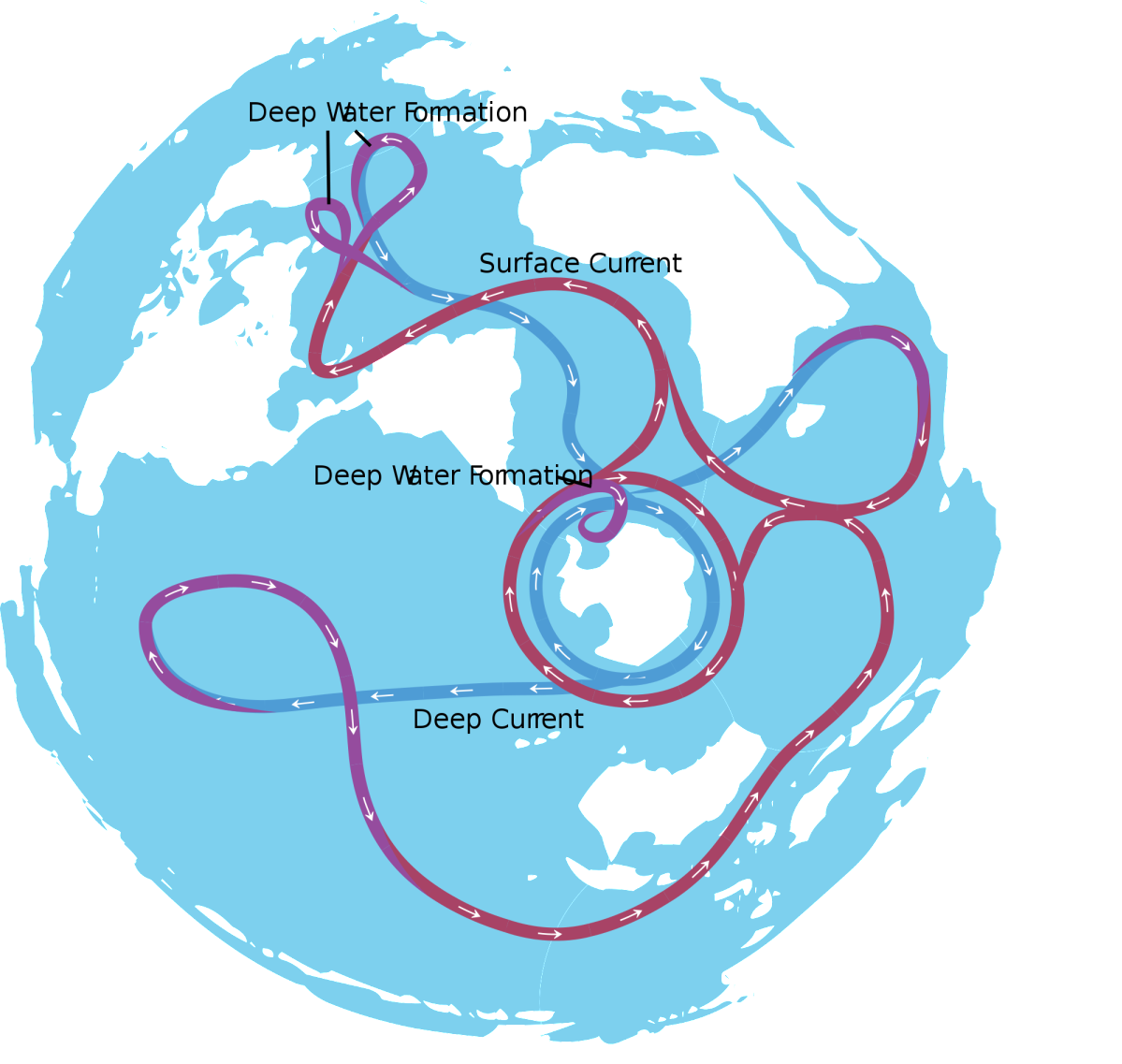
Hydrological regime. Surface currents in the Atlantic Ocean, they are represented by two extensive anticyclonic gyres with centers of about 30 ° north and south latitude.
The northern subtropical circulation forms the North Passat, Antilles, Florida, Gulf Stream, North Atlantic and Canary currents, the southern - South Passat, Brazilian, West Winds and Benguela. Between these cycles there is an Equatorial backflow (at 5-10 ° N), which in the east passes into Guinea. A subsurface counterflow of Lomonosov is located under the South Tradewind Current. It crosses the ocean from west to east at a depth of 300-500 m, reaches Guinea Bay is located and fades to the south of it. Under the Gulf Stream at a depth of 900-3500 m, at a speed of up to 20 km / h, there is a powerful subsurface Western Frontier bottom counter-flow, the formation of which is associated with the bottom flow of cold waters from high latitudes. In the northwest Atlantic, a cyclonic gyre is distinguished, consisting of the North Atlantic, Irminger, East Greenland, West Greenland and Labrador currents. In the eastern part of the Atlantic Ocean, the deep Lusitanian current is well defined, formed by the bottom flow of Mediterranean waters through the Strait of Gibraltar.
Excitementin the Atlantic Ocean depends on the direction, duration and speed of the prevailing winds. The region of greatest wave activity is located north of 40 ° C. sh. and south of 40 ° S. sh. The height of the waves during long and very winds sometimes reaches 22-26 m. Comparatively often there are waves with a height of 10-15 m. Annually during the passage of tropical cyclones, waves with a height of 14-16 m are formed. In the northern part of the Atlantic in the Antilles islands and off the coast of Portugal are often observed storm surges 2-4 m in height.
In most of the Pacific tidessemi-daily. In the open ocean, the height of the tide usually does not exceed 1 m (St. Helena - 0.8 m, Ascension Island - 0.6 m). Along the coast of Europe in the Bristol Bay, the tides reach 15 m, the Gulf of Saint-Malo - 9-12 m. They reach the highest magnitude in the Bay of Fundy, where the highest tide in the world is 18 m, with a tidal current of up to 5.5 m / with.
Average annual surface water temperature The Atlantic Ocean is 16.9 ° C. Its annual amplitude in equatorial tropical latitudes is no more than 1-3 ° С, subtropical and temperate latitudes is 5-8 ° С, polar is about 4 ° С in the north and up to 1 ° С in the south. In general, the temperature of the surface waters of the Atlantic decreases from the equator to high latitudes. In winter, in February in the Northern Hemisphere and in August in the Southern: it varies from +28 ° C at the equator to +6 ° C at 60 ° N. and -1 ° C at 60 ° S. sh., in summer, in August in the Northern Hemisphere and in February in the Southern: from +26 ° С at the equator to +10 ° С at 60 ° N. lat. and about 0 ° C at 60 ° S. sh. Ocean currents cause significant anomalies of surface water temperature. The northern part of the ocean due to the significant influx of warm waters from low latitudes is significantly warmer than its southern part. In some regions along the coasts of the continents, differences in the water temperature of the western and eastern sectors of the ocean are observed. So, at 20 °. sh. the presence of warm currents maintains the water temperature in the west of the ocean at 27 ° C, while in the east it is only 19 ° C. In places where cold and warm currents meet, significant horizontal temperature gradients of the surface layer are observed. At the junction of the East Greenland and Irminger currents, a temperature difference of 7 ° C within a radius of 20-30 km is common.
The Atlantic Ocean is the saltiest of all the oceans. Average salinityits waters is 35.4 ‰. The highest salinity of waters up to 37.9 is observed in tropical latitudes in the east of the Atlantic, where there is little precipitation and maximum evaporation. In the equatorial zone, the salinity decreases to 34-35, in high latitudes - drops to 31-32. The zonal salinity distribution is often disturbed as a result of the movement of water by currents and the inflow of fresh water from land.
Ice formation in the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean occurs mainly in the internal seas of temperate latitudes (Baltic, North, Azov) and the Gulf of St. Lawrence. A large number of floating ice and icebergs from the Arctic Ocean are carried into the open ocean. Floating ice in the northern hemisphere even reaches 40 ° C in July. sh. In the south of the Atlantic, ice and icebergs form in Antarctic waters. The main source of icebergs is the Filchner Ice Shelf in the Weddell Sea. South 55 ° S. sh. floating ice is present throughout the year.
Water clarity in the Atlantic Ocean varies widely. It decreases from the equator to the poles and from the coasts to the central part of the ocean, where the water is usually uniform and transparent. The maximum transparency of the water in the Weddell Sea is 70 m, the Sargasso is 67 m, the Mediterranean is 50, the Black one is 25 m, and the North and Baltic are 18-13 m.
Surface water masses in the Atlantic Ocean, they range in thickness from 100 m in the southern hemisphere to 300 m in equatorial-tropical latitudes. They are distinguished by significant seasonal variability of properties, vertical uniformity of temperature, salinity and density. Subsurface waters fill depths up to about 700 m and differ from surface waters by increased salinity and density.
Intermediate water masses in the northwestern part of the ocean are formed as a result of the immersion of cold waters coming from high latitudes. A special aqueous intermediate mass is formed by saline waters from the Mediterranean Sea. In the Southern Hemisphere, intermediate water is formed by lowering the cooled Antarctic waters and is characterized by low temperature and low salinity. It moves north first at a depth of 100–200 m, gradually sinking north of 20 °. sh. at a depth of 1000 m mixed with the northern intermediate water.
The deep water masses of the Atlantic Ocean consist of two layers of different genesis. The upper horizon is formed by lowering the warm and salty Mediterranean waters. In the northern part of the ocean, it is located at depths of 1000–1250 m, in the Southern Hemisphere it drops to 2500–750 m and marks 45 ° south. sh. The lower layer of deep water is formed mainly as a result of immersion of the cold waters of the East Greenland current from depths of 2500-3000 m in the northern hemisphere to 3500-4000 m at 50 ° S. sh. where it begins to be ousted by the Antarctic bottom waters.
Bottom water masses form mainly on the Antarctic shelf and gradually spread over the ocean floor. North of 40 ° N the presence of bottom water coming from the Arctic Ocean is noted. They are characterized by uniform salinity (34.6-34.7) and low temperature (1-2 ° С).
Organic world. The Atlantic Ocean is inhabited by various species of plants and animals. Brown and red algae are characteristic of the phytobenthos of the temperate and polar latitudes of the Atlantic. In the equatorial-tropical zone, phytobenthos is represented by numerous green algae (caulerpa, valonia, and others) of red predominant lithothamia, of brown algae - sargasso. On the littoral of the European coast is widely represented sea grass - Zoster.
The phytoplankton of the Atlantic Ocean has 245 species. They are represented by an approximately equal number of peridinous species, coccolithophores and diatoms. The latter have a distinct zonal distribution and live mainly in temperate latitudes. The fauna of the Atlantic has fewer species than in the Pacific Ocean. But some families of fish (cod, herring, etc.) and mammals (seals, etc.) are represented much richer in the Atlantic Ocean. The total number of species of whales and pinnipeds is about 100, fish are more than 15,000. Of the birds, albatrosses and petrels are common. The distribution of animal organisms has a well-pronounced zonal character, while not only the number of species, but also the total biomass is zonal changing.
In the sub-Antarctic and temperate latitudes, biomass reaches a maximum, but the number of species is much smaller than in the equatorial-tropical zone. Antarctic waters are poor in species and biomass. The fauna of the sub-Antarctic and temperate zones of the southern Atlantic Ocean is dominated by: copepods and pteropods in zooplankton, whales and pinnipeds among mammals, and notothenian ones from fish. In temperate latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, foraminifera and copepods are most characteristic of zooplankton. Of the commercial fish, herring, cod, haddock, halibut, sea bass are of the greatest importance.
In the equatorial tropical zone, zooplankton consists of numerous species of foraminifera and pterapod, several species of radiolarians, copepods, mollusk larvae and fish. Sharks, flying fish, sea turtles, jellyfish, squids, octopuses, corals are characteristic of these latitudes. Commercial fish are represented by mackerel, tuna, sardines, and anchovy.
The deep-water fauna of the Atlantic Ocean is represented by crustaceans, echinoderms, specific genera and families of fish, sponges, hydroids. The endemic species of polychaetes, isopods and sea cucumbers live in ultra-abyssals.
In the Atlantic Ocean, four biogeographic regions are distinguished: the Arctic, North-Atlantic, Tropico-Atlantic and Antarctic. Fish in the Arctic region are characterized by haddock, cod, herring, saury, sea bass, and halibut; North Atlantic - cod, haddock, pollock, various flatfish, in the more southern areas - wrasse, mullet, sultan; Tropic-Atlantic - sharks, flying fish, tuna, etc .; Antarctic - nototenevye.
In the Atlantic Ocean are the following physiographic zones and areas. Northern subpolar belt: Labrador basin, Danish strait and waters of Southeastern Greenland, Davis Strait; north temperate belt: area of the American shelf, the Gulf of St. Lawrence, the English Channel and the Pas de Calais, the Irish Sea, the Celtic Sea, the North Sea, the Danish (Baltic) Straits, the Baltic Sea; northern subtropical belt: Gulf Stream, Priibraltar region, Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea Straits and the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov; northern tropical belt: West African region, American Mediterranean with subareas: Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, Bahamas subdistrict; equatorial belt: Gulf of Guinea, Western Shelf; southern tropical belt: district of the Congo; southern subtropical belt: La Plata district, South-West Africa region; south temperate belt: Patagonian District; southern subpolar belt: Scotia Sea; south polar zone: Weddell Sea.
Atlantic Ocean is an second largest ocean of the planet. It is located between Greenland and Iceland in the north, Europe and Africa in the east, North and South America in the west and Antarctica in the south. The coastal line of the ocean is heavily indented in the Northern Hemisphere and weakly in the Southern. The greatest depth is 8742 m in the chute Puerto Rico.
The area of the Atlantic Ocean with its seas is 91.6 million km 2, the average depth is 3332 m, the maximum depth is 8742 m.
The Atlantic Ocean was formed after the collapse of Gondwana and Laurasia (in the Mesozoic), it is relatively young. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge stretches across the ocean in the meridional direction, which divides it into western and eastern parts.
The Atlantic Ocean is located in almost all climatic zones, except for the Arctic, but most of it lies in areas of equatorial, subequatorial, tropical and subtropical climates. In the temperate latitudes of the Northern hemisphere, strong westerly winds dominate, but they reach their greatest strength in the temperate latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. In the subtropic and tropical latitudes, trade winds dominate.
In the Atlantic Ocean, currents directed almost in the meridional direction are well expressed. This is due to the large elongation of the ocean from north to south and the outlines of its coastline. The most known warm current Gulf Stream and its continuation - North Atlantic flow.
The salinity of the ocean as a whole is higher than the average salinity of the waters of the World Ocean, and the organic world is poorer in terms of biodiversity in comparison with the Pacific Ocean.
Since ancient times, the Atlantic Ocean has been mastered by people and is now considered the most developed. Important sea lanes connecting Europe and North America and both these parts of the world with the oil countries of the Persian Gulf pass through the Atlantic. The shelves of the North Sea and the Gulf of Mexico are pre-oil sites. Material from the site
The seas of the Atlantic Ocean are the main fishing areas, and up to half of the global fish catch is caught here. The main fishing areas are the shelves, i.e., relatively shallow ocean areas. The commercial value of the rural fish (herring, sardines), cod (cod, haddock, navaga), mackerel, flounder, halibut, grouper, eel, sprats, etc. (Fig. 60). Unfortunately, stocks of Atlantic herring and cod, sea bass and other species of fish have sharply decreased. Today, the problem of preserving the biological and mineral resources of not only the Atlantic, but also the rest of the oceans is particularly acute. The fishing countries of the world agree on the allowable catch of fish and measures to combat poachers.
Atlantic Ocean - the second largest ocean after the Pacific. It contains 25% of the entire water of the planet. The average depth is 3,600 meters. The maximum depth is in the Puerto Rico Trench - 8,742 meters. The ocean area is 91 million square meters. km
general information
The ocean arose as a result of the split of the supercontinent. Pangea»Into two large parts, which subsequently formed in the modern continents.
The Atlantic Ocean is known to man since ancient times. Mentioning the ocean, which " referred to as the Atlantic", Can be found in the records 3 in. BC. The name probably originated from the legendary missing mainland " Atlantis«.

The truth is not clear what territory he designated, because in ancient times, people were limited in means of transportation by sea.
Relief and Islands
A distinctive feature of the Atlantic Ocean is a very small number of islands, as well as a complex relief of the bottom, which forms many trenches and trenches. The deepest among them are the trough of Puerto Rico and South Sandwich, the depth of which exceeds 8 km.

Earthquakes and volcanoes have a great impact on the structure of the bottom, the greatest activity of tectonic processes is observed in the equatorial zone.
 Volcanic activity in the ocean continues for 90 million years. The height of many underwater volcanoes exceeds 5 km. The largest and most famous are found in the gutters of Puerto Rico and Juno-Sandwich, as well as on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Volcanic activity in the ocean continues for 90 million years. The height of many underwater volcanoes exceeds 5 km. The largest and most famous are found in the gutters of Puerto Rico and Juno-Sandwich, as well as on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Climate
The large meridional extent of the ocean from north to south explains the diversity of climatic conditions on the ocean surface. In the equatorial zone, slight temperature fluctuations throughout the year and an average of +27 degrees. There is also a huge influence on ocean temperature by the exchange of water with the Arctic Ocean. From the north, tens of thousands of icebergs drift into the Atlantic Ocean, reaching almost to tropical waters.

The Gulf Stream is emerging along the southeastern coast of North America - the largest current on the planet. Water consumption per day is 82 million cubic meters, which is 60 times more than the flow of all rivers. The width of the current reaches 75 km. in width, and a depth of 700 m. The speed of the flow ranges from 6-30 km / h. The Gulf Stream carries warm waters, the temperature of the upper layer of the flow is 26 degrees.
In the area of. The Newfoundland Gulf Stream meets the “cold wall” of the Labrador Current. The mixing of water creates ideal conditions for the reproduction of microorganisms in the upper layers. Best known in this regard Big Newfoundland Barrel, being a source of fishing for such fish as cod, herring and salmon.
Flora and fauna
The Atlantic Ocean is characterized by an abundance of biomass with a relatively poor species composition in the northern and southern margins. The greatest species diversity is observed in the equatorial zone.
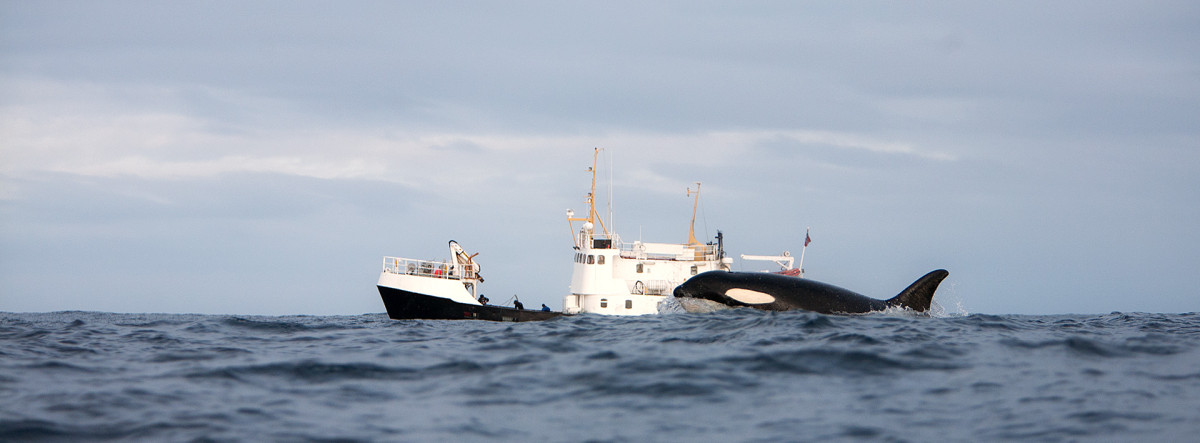

Of the fish, the most common are the family of nanomeny and proteinaceous pikes. Large mammals are most widely represented: cetaceans, seals, fur seals, etc. The amount of plankton is insignificant, which causes the migration of whales to the feeding fields to the north or to temperate latitudes, where it is more.

Many places in the Atlantic Ocean have been and continue to be intense fishing grounds. Earlier, the development of the ocean led to the fact that hunting for mammals has been spread here for a long time. This reduced the number of certain species of animals compared to the Pacific and Indian oceans. 
Plants are represented by a wide range of green, brown and red algae. Famous Sargassians form the Sargasso Sea, which is popular from books and interesting stories.

New Articles
- What is the highest peak of the Ural Mountains
- The most ancient religions in the world
- What continents are washed by the Atlantic Ocean?
- Can I wear jewelry of the deceased?
- Snake, Bowl and Staff: The Origin of Medical Symbols
- Interesting facts about hares
- Names of famous brands in other countries
- Karelo Finnish epic kalevala protagonists
- 17 18 weeks pregnant sensations
- Why do people become so aggressive
Popular articles
- Expression twice in one river, meaning and meaning
- Gusli - musical instruments
- Report: Temperature Scales and Thermometers
- Which side to sew on chevron
- How to draw emblems for school
- Unusual rivers of the world and the rivers of Russia - Rivers with sour water
- Numb of the little finger on the right hand: causes and methods of treatment
- Why development is important for a person
- Constellations from ancient atlases
- What happens at 31 weeks
